南湖新聞網訊(通訊員 楊嘉成)近日,我校農(nong) 業(ye) 微生物資源發掘與(yu) 利用全國重點實驗室、動物育種與(yu) 健康養(yang) 殖前沿科學中心、湖北洪山實驗室、動科動醫學院孫鋁輝教授課題組在《Science Advances》期刊上發表了題為(wei) “Loss of SELENOW aggravates muscle loss with regulation of protein synthesis and ubiquitin-proteasome system”的研究論文。該研究首次揭示了硒蛋白W(SELENOW)在肌肉萎縮中的重要功能及機製。

硒是人和動物所必需的微量元素,主要以25個(ge) 硒蛋白的形式發揮生物學功能。然而,我國有超過2/3以上的國土麵積存在硒的缺乏,導致人和動物均麵臨(lin) 著營養(yang) 性缺硒的風險。在集約化的畜禽養(yang) 殖業(ye) 中,高密度飼養(yang) 、熱應激、有害氣體(ti) 及黴菌毒素等多種應激源常使動物處於(yu) 亞(ya) 健康狀態,使得畜禽對硒的需要量升高,嚴(yan) 重情況下,甚至誘發群體(ti) 性營養(yang) 性缺硒疾病的發生,如缺硒性肌營養(yang) 不良症(NMD),它會(hui) 引起動物生長發育的遲緩和肉品質下降,給養(yang) 殖業(ye) 造成巨大經濟損失。
課題組前期研究發現,缺硒誘導肉雞NMD發生與(yu) 肌肉中一碳代謝紊亂(luan) 誘導機體(ti) 免疫係統和氧化還原穩態失衡相關(guan) ,其中,SELENOW在此過程中下調尤為(wei) 顯著(JournalofNutrition,2023)。然而,SELENOW在NMD發生中的作用與(yu) 機製尚不清楚。因此,本研究係統性探究了SELENOW在肌肉中的功能。研究結果表明,正常生理條件下,SELENOW的缺失並不影響動物的生長和肌肉的發育;在地塞米鬆誘導的急性肌肉萎縮和自然衰老相關(guan) 的慢性肌肉萎縮條件下,SELENOW會(hui) 表達上調,然而,SELENOW的缺失會(hui) 加劇此萎縮條件下肌肉質量的流失;體(ti) 內(nei) 外過表達SELENOW,可緩解地塞米鬆誘導的肌管和肌肉萎縮。
進一步的機製研究表明,SELENOW通過與(yu) RAC1蛋白互作,調控RAC1-mTOR級聯信號通路。當SELENOW缺失時,通過抑製RAC1-mTOR級聯導致肌肉內(nei) 蛋白質合成減少,泛素化降解加速,從(cong) 而加劇了肌肉萎縮的進程。
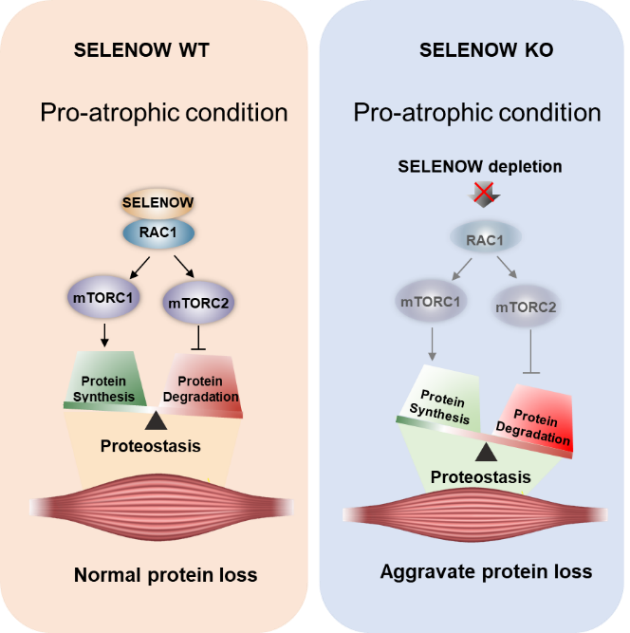
圖1 SELENOW通過調控RAC1-mTOR級聯參與(yu) 蛋白質穩態調節
本研究揭示了SELENOW缺失通過抑製RAC1-mTOR級聯加劇肌肉萎縮。研究結果為(wei) 合理應用硒防控畜禽NMD提供了新的科學依據,也為(wei) 預防和治療人類肌肉萎縮提供了潛在的靶點。
星空体育网站入口官网動科動醫學院已畢業(ye) 博士楊嘉成(現為(wei) 動科動醫學院博士後)為(wei) 論文第一作者,孫鋁輝教授為(wei) 論文的通訊作者。美國康奈爾大學雷新根教授、湖北省農(nong) 業(ye) 科學院魏金濤副研究員等也參與(yu) 了本項研究。該研究得到科技創新2030-重大項目、青年拔尖人才支持計劃、國家自然科學基金和中央高校基礎研究基金的支持。
【英文摘要】
Sarcopenia is characterized by accelerated muscle mass and function loss, which burdens and challenges public health worldwide. Several studies indicated that selenium deficiency is associated with sarcopenia; however, the specific mechanism remains unclear. Here, we demonstrated that selenoprotein W (SELENOW) containing selenium in the form of selenocysteine functioned in sarcopenia. SELENOW expression is up-regulated in dexamethasone (DEX)–induced muscle atrophy and age-related sarcopenia mouse models. Knockout (KO) of SELENOW profoundly aggravated the process of muscle mass loss in the two mouse models. Mechanistically, SELENOW KO suppressed the RAC1-mTOR cascade by the interaction between SELENOW and RAC1 and induced the imbalance of protein synthesis and degradation. Consistently, overexpression of SELENOWin vivoandin vitroalleviated the muscle and myotube atrophy induced by DEX. SELENOW functioned in age-related sarcopenia and regulated the genes associated with aging. Together, our study uncovered the function of SELENOW in age-related sarcopenia and provides promising evidence for the prevention and treatment of sarcopenia.
審核人 彭貴青
【文章鏈接】: