南湖新聞網訊(通訊員 胡軍(jun) ) 近日,The ISME Journal雜誌在線發表了我校農(nong) 業(ye) 微生物資源發掘與(yu) 利用全國重點實驗室、教育部動物育種與(yu) 健康養(yang) 殖前沿科學中心、湖北洪山實驗室晏向華教授課題組的研究成果,論文題為(wei) “Characterizing core microbiota and regulatory functions of the pig gut microbiome”。該研究構建了豬腸道微生物參考基因集,篩選到豬腸道核心優(you) 勢細菌,並解析其對宿主代謝的調控作用機製,對實施腸道菌群幹預改善豬生長與(yu) 腸道健康具有重要意義(yi) 。
我國是生豬養(yang) 殖大國,生豬存欄量居世界首位,擁有70多個(ge) 地方豬品種,具有豐(feng) 富的地方豬資源。已有研究表明腸道微生物與(yu) 豬的腹瀉抗性、飼料轉化效率、肉品質和免疫功能等重要表型具有密切聯係。然而,針對我國特色地方豬腸道微生物資源的發掘與(yu) 利用仍顯不足。因此,全麵係統地解析我國豬腸道微生物區係的組成與(yu) 功能對發掘功能微生物和解析其與(yu) 宿主的互作機製具有重要意義(yi) 。
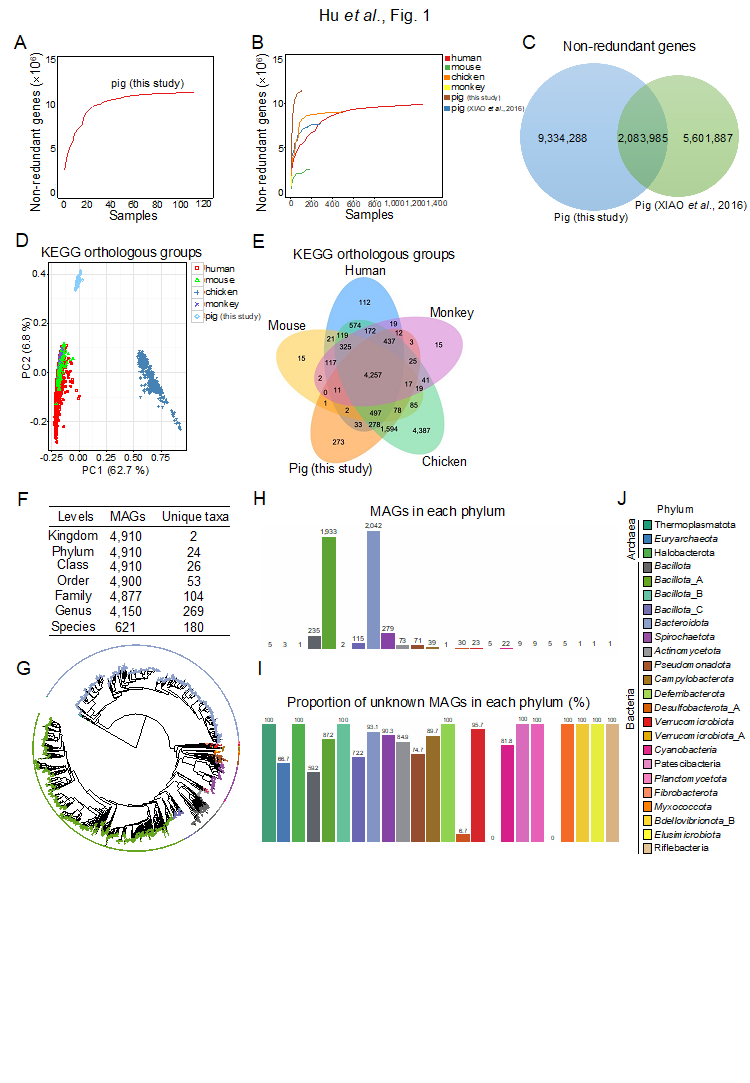
研究人員綜合運用宏基因組學和細菌16S rDNA擴增子測序技術係統解析了7個(ge) 品種豬(即杜×(長×大)豬、藏豬、萊蕪豬、沙子嶺豬、從(cong) 江香豬、環江香豬和寧鄉(xiang) 豬)共計56頭斷奶仔豬和56頭育肥末期豬的腸道微生物區係組成。鑒定了11418273個(ge) 非冗餘(yu) 腸道微生物基因,通過與(yu) 已發表文獻的非冗餘(yu) 腸道微生物基因進行整合,本研究構建了包含17020160個(ge) 非冗餘(yu) 基因的豬腸道微生物基因集,通過對宏基因組組裝數據進行分箱,共重構獲得了4910個(ge) 非冗餘(yu) 原核微生物基因組。研究表明我國地方豬腸道微生物的營養(yang) 物質(包括脂類、氨基酸、碳水化合物和核苷酸)代謝能力和能量代謝能力比杜×(長×大)商品豬更強。杜×(長×大)商品豬腸道微生物的抗生素抗性基因豐(feng) 度比中國地方豬更高,研究發現品種和日齡是影響豬腸道微生物區係組成和功能的關(guan) 鍵因素。綜合評估微生物的出現率、微生物相對豐(feng) 度和豬生長階段,利用宏基因組學和細菌16S rDNA擴增子測序共鑒定出3種豬腸道核心優(you) 勢細菌(Phascolarctobacterium succinatutens、Prevotella copri和Oscillibacter valericigenes),結果表明灌服上述3種核心優(you) 勢細菌可顯著增加無菌小鼠的器官指數(包括心髒、脾髒和胸腺),降低胃腸道的長度,增強腸道上皮屏障功能,增加腸道的隱窩深度,同時上述3種核心優(you) 勢細菌可顯著改變無菌小鼠的營養(yang) 物質代謝過程(包括初級膽汁酸的生物合成、苯丙氨酸、酪氨酸和色氨酸的生物合成、苯丙氨酸的代謝等)。綜上,本研究係統性解析了7個(ge) 品種豬的腸道微生物的組成與(yu) 功能,篩選出豬腸道微生物核心優(you) 勢細菌並證明了其對無菌小鼠器官指數、腸道屏障功能、腸道黏膜形態和營養(yang) 物質代謝的關(guan) 鍵調控作用,為(wei) 實施腸道菌群幹預改善豬生長與(yu) 腸道健康提供理論依據和新資料。
星空体育网站入口官网博士後胡軍(jun) 為(wei) 第一作者,王湘如教授和晏向華教授為(wei) 共同通訊作者。本研究由星空体育网站入口官网生豬精準飼養(yang) 團隊牽頭,聯合貴州大學張勇副教授、中國科學院亞(ya) 熱帶農(nong) 業(ye) 生態研究所孔祥峰研究員、湖南農(nong) 業(ye) 大學黃興(xing) 國教授和中國農(nong) 業(ye) 科學院深圳農(nong) 業(ye) 基因組研究所唐中林研究員開展係統性研究,是一個(ge) 多方協同攻堅的成果。本研究得到國家自然科學基金、博士後創新人才計劃、博士後麵上項目、湖北省自然科學基金的資助。
英文摘要:
Domestic pigs (Sus scrofa) are the leading terrestrial animals used for meat production. The gut microbiota significantly affect host nutrition, metabolism, and immunity. Hence, characterization of the gut microbial structure and function will improve our understanding of gut microbial resources and the mechanisms underlying host-microbe interactions. Here, we investigated the gut microbiomes of seven pig breeds using metagenomics and 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. We established an expanded gut microbial reference catalog comprising 17,020,160 genes and identified 4,910 metagenome-assembled genomes (MAGs). We also analyzed the gut resistome to provide an overview of the profiles of the antimicrobial resistance genes in pigs. By analyzing the relative abundances of microbes, we identified three core-predominant gut microbes (Phascolarctobacterium succinatutens, Prevotella copri, and Oscillibacter valericigenes) in pigs used in this study. Oral administration of the three core-predominant gut microbes significantly increased the organ indexes (including the heart, spleen, and thymus), but decreased the gastrointestinal lengths in germ-free (GF) mice. The three core microbes significantly enhanced intestinal epithelial barrier function and altered the intestinal mucosal morphology, as was evident from the increase in crypt depths in the duodenum and ileum. Furthermore, the three core microbes significantly affected several metabolic pathways (such as “steroid hormone biosesynthesis”, “primary bile acid biosesynthesis”, “phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan biosesynthesis”, and “phenylalanine metabolism”) in GF mice. These findings provide a panoramic view of the pig gut microbiome and insights into the functional contributions of the core-predominant gut microbes to the host.
審核人:王湘如 晏向華