(通訊員:朱碩)近日,我校動物科學技術與(yu) 動物醫學院曹勝波教授、葉靜教授團隊在Journal of Neuroinflammation雜誌上發表了題為(wei) “H3K27me3 of Rnf19a promotes neuroinflammatory response during Japanese encephalitis virus infection”的研究論文。該研究首次發現了表觀遺傳(chuan) 修飾在日本腦炎病毒誘導的神經炎症中發揮重要作用,闡明了Rnf19a調控日本腦炎病毒誘導神經炎症反應的分子機製,為(wei) 尋找日本腦炎治療藥物靶點提供新的線索。
日本腦炎是由日本腦炎病毒(Japanese encephalitis virus infection, JEV)感染引起的蚊媒傳(chuan) 播人畜共患傳(chuan) 染病,該病主要引起種豬的繁殖障礙,導致母豬流產(chan) ,公豬睾丸炎,對我國養(yang) 殖業(ye) 造成巨大經濟損失。同時JEV還可由豬經蚊向人傳(chuan) 播,引起人神經係統疾病,嚴(yan) 重可造成致死性腦炎,但該病毒引起中樞神經係統炎症反應的分子機製仍有待闡明。
研究人員首先發現JEV感染會(hui) 導致小鼠小膠質細胞係BV2、原代膠質細胞和小鼠腦組織中H3K27me3水平明顯上調,並利用甲基化轉移酶EZH2抑製劑證明H3K27me3修飾可能在JEV誘導的小膠質細胞炎症中發揮重要的調控作用。
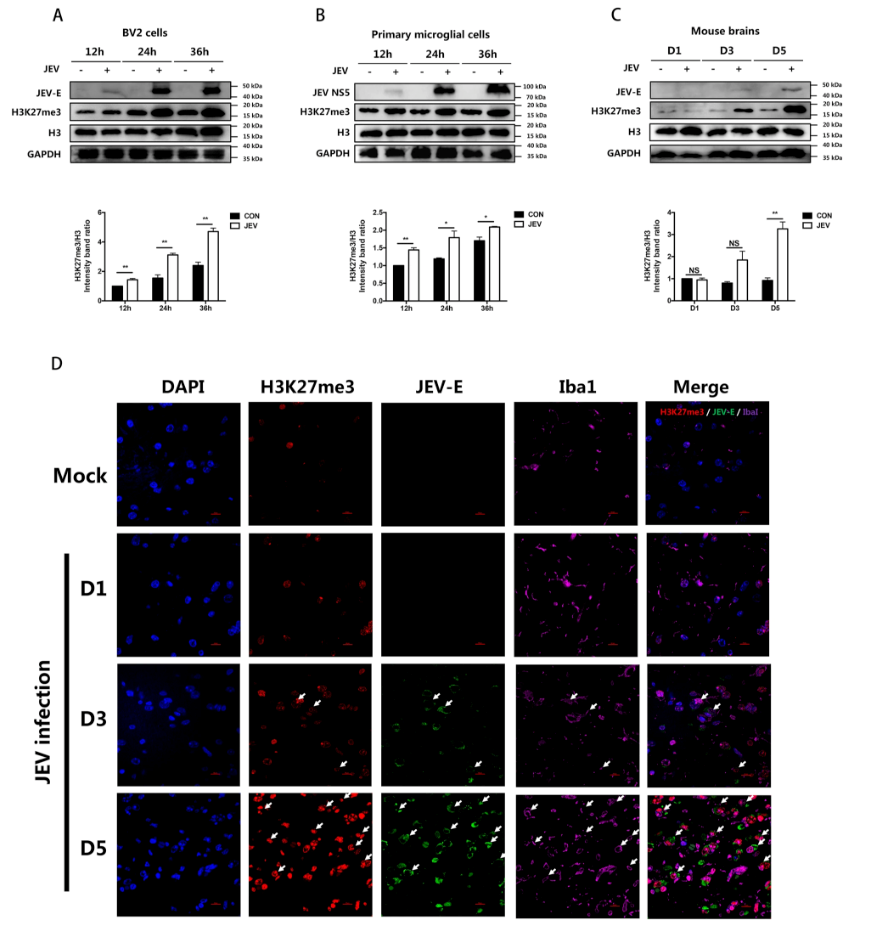
圖1. JEV感染引起小鼠小膠質細胞係BV2、原代膠質細胞和小鼠腦組織中H3K27me3水平上調
隨後,研究人員利用ChIP-Sequencing分析JEV感染細胞中H3K27me3所參與(yu) 調控的基因,最終篩選出JEV感染後炎症抑製性基因Rnf19a啟動子區域對應的H3K27me3修飾明顯上調,而Rnf19a表達量明顯下降。隨後通過使用基因敲除和過表達手段,證明了Rnf19a在JEV誘導的小膠質細胞炎症反應中起負調控作用。進一步實驗證明E3泛素連接酶Rnf19a是通過泛素化降解RIG-I從(cong) 而抑製炎症反應。以上研究結果表明JEV可通過上調Rnf19a啟動子區域H3K27me3修飾,抑製該基因表達,從(cong) 而促進炎症反應的發生。
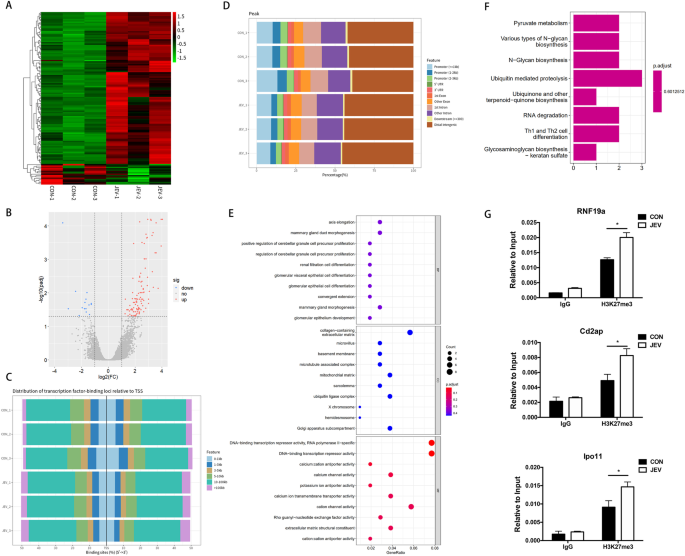
圖2.ChIP-Sequencing分析JEV感染細胞中H3K27me3參與(yu) 調控的基因
我校動科動醫學院研究生朱碩和陶夢穎為(wei) 論文共同第一作者,葉靜教授為(wei) 論文通訊作者。該研究得到國家自然科學基金、國家重點研發計劃項目等項目資助。
【英文摘要】
Histone methylation is an important epigenetic modification that affects various biological processes, including the inflammatory response. In this study, we found that infection with Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) leads to an increase in H3K27me3 in BV2 microglial cell line, primary mouse microglia and mouse brain. Inhibition of H3K27me3 modification through EZH2 knockdown and treatment with EZH2 inhibitor significantly reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines during JEV infection, which suggests that H3K27me3 modification plays a crucial role in the neuroinflammatory response caused by JEV infection.The chromatin immunoprecipitation-sequencing (ChIP-sequencing) assay revealed an increase in H3K27me3 modification of E3 ubiquitin ligases Rnf19a following JEV infection, which leads to downregulation of Rnf19a expression. Furthermore, the results showed that Rnf19a negatively regulates the neuroinflammatory response induced by JEV. This is achieved through the degradation of RIG-I by mediating its ubiquitination. In conclusion, our findings reveal a novel mechanism by which JEV triggers extensive neuroinflammation from an epigenetic perspective.
原文連接:
審核人:葉靜